Contents
1.NioEndPoint简介
TCP/IP请求到达后,EndPoint负责处理TCP/IP请求,并且交给对应的处理器处理,本篇中讨论将范围限制在Http11NioProtocal中,所以处理的就是http请求。 根据命名可以知道它采用了非阻塞I/O的模式。值得一提,tomcat从8.5开始Connector取消了BIO模式的支持。
NioEndPoint在Tomcat的Connector中所处的位置:
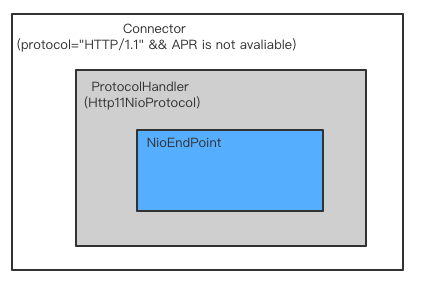
NioEndPoint是一款NIO定制的线程池,提供以下服务:
- Socket acceptor 线程
- Socket poller 线程
- Worker 线程池
2.NioEndPoint内部组成
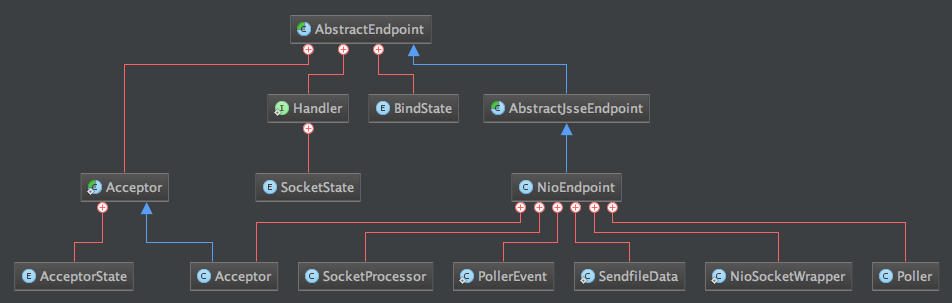
NioEndPoint的继承关系如下图所示:
3.NioEndPoint内部处理
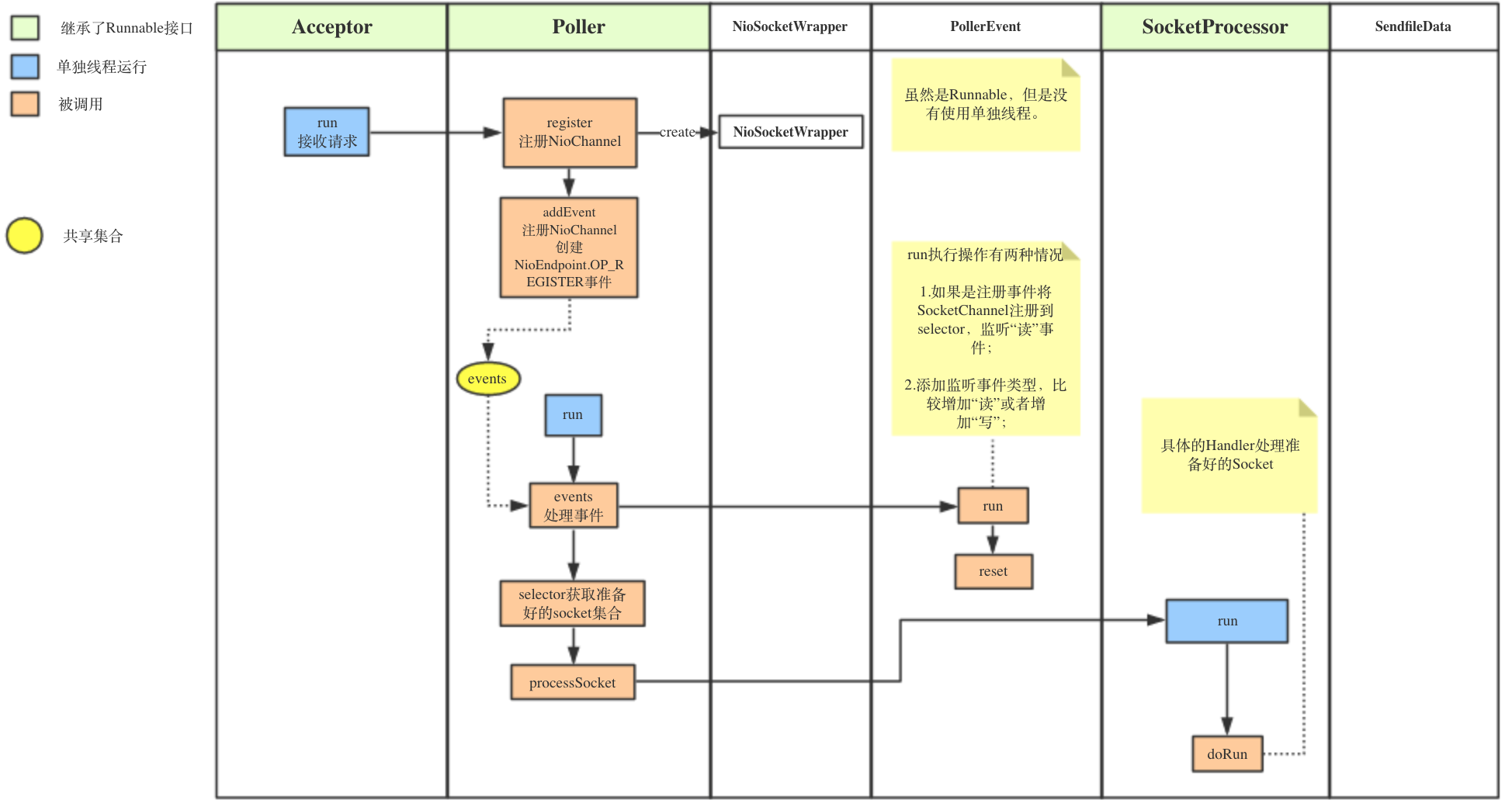
下图显示的是NioEndPoint内部几条主要的处理过程,这里为了便于理解处理流程,做了简化处理。主要分成三条处理路径,反应在图上的三个蓝色起点。具体解释看小标题内容。
3.1 Acceptor 接收请求
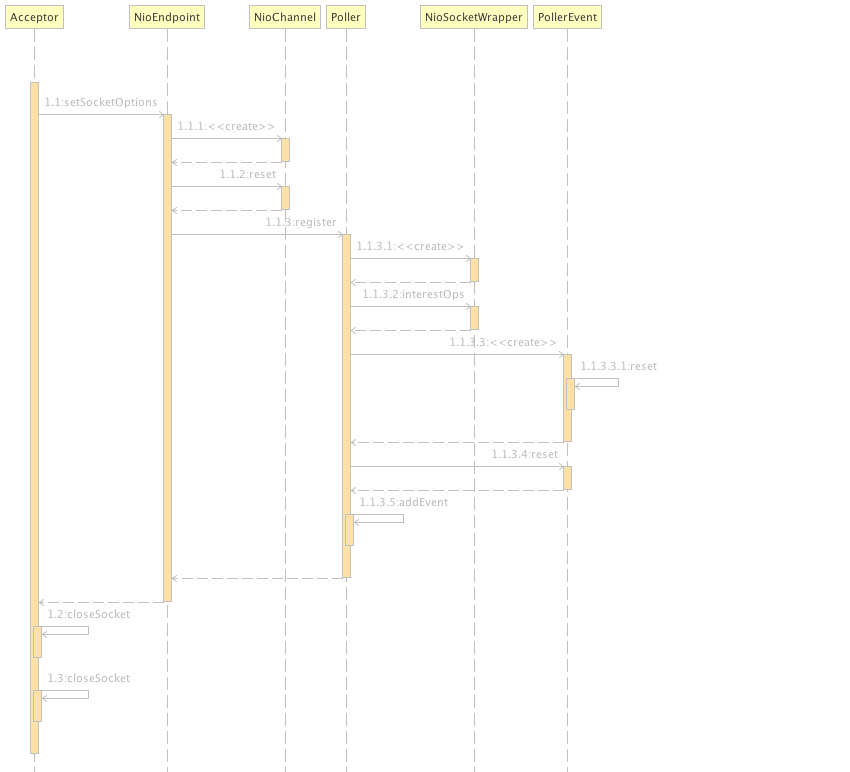
Acceptor接收请求本质上是调用java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel中的accept创建与客户端连接的socket(事实上对应类java.nio.channels.SocketChannel),并且使用NioChannel 进行包装。NioChannel是tomcat中创建的SocketChannel的包装器,用于屏蔽SSL与非SSL的不同。调用Poller的registor方法注册NioChannel。创建Poller的注册事件到并且添加到events集合。下面图是这个调用过程的顺序图。
3.2 处理Poller事件
3.1步骤中加入了注册事件、除此之外还有读和写事件等。Poller每次执行run首先查看events需要处理的事件,对于注册事件调用java.nio.channels.spi.AbstractSelectableChannel的register方法将SocketChannel注册到selector中。对于其它类型的事件则追加事件到selector监听的配置中。处理完事件后,开始查看注册在selector中的channel有没有准备好的,有的话调用processSocket进行处理。下面图是这个调用过程的顺序图。
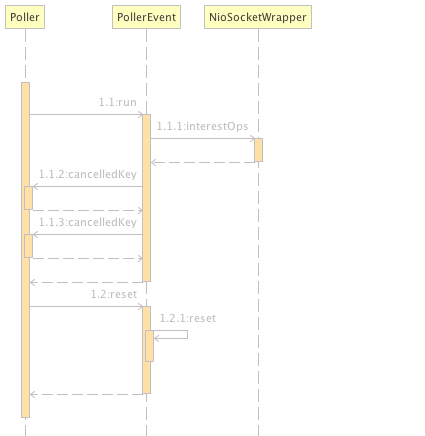
3.3 SocketProcessor处理Socket
这个步骤就是将socket交给后续的Handler进行处理。本次例子中就是Http11NioProtocol了。下面是本操作的具体代码。
/**
* This class is the equivalent of the Worker, but will simply use in an
* external Executor thread pool.
*/
protected class SocketProcessor extends SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> {
public SocketProcessor(SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event) {
super(socketWrapper, event);
}
@Override
protected void doRun() {
NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket();
SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());
try {
int handshake = -1;
try {
if (key != null) {
if (socket.isHandshakeComplete()) {
// No TLS handshaking required. Let the handler
// process this socket / event combination.
handshake = 0;
} else if (event == SocketEvent.STOP || event == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT ||
event == SocketEvent.ERROR) {
// Unable to complete the TLS handshake. Treat it as
// if the handshake failed.
handshake = -1;
} else {
handshake = socket.handshake(key.isReadable(), key.isWritable());
// The handshake process reads/writes from/to the
// socket. status may therefore be OPEN_WRITE once
// the handshake completes. However, the handshake
// happens when the socket is opened so the status
// must always be OPEN_READ after it completes. It
// is OK to always set this as it is only used if
// the handshake completes.
event = SocketEvent.OPEN_READ;
}
}
} catch (IOException x) {
handshake = -1;
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Error during SSL handshake",x);
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
handshake = -1;
}
if (handshake == 0) {
SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;
// Process the request from this socket
if (event == null) {
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ);
} else {
state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event);
}
if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) {
close(socket, key);
}
} else if (handshake == -1 ) {
close(socket, key);
} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_READ){
socketWrapper.registerReadInterest();
} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE){
socketWrapper.registerWriteInterest();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException cx) {
socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);
} catch (VirtualMachineError vme) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(vme);
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("", t);
socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);
} finally {
socketWrapper = null;
event = null;
//return to cache
if (running && !paused) {
processorCache.push(this);
}
}
}
} 4.参考
http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.5-doc/index.html
tomcat8.5源码